The digital revolution has transformed every aspect of modern life, but it comes with an environmental cost that can no longer be ignored. As our world becomes increasingly connected and data-dependent, the infrastructure supporting this digital ecosystem is consuming unprecedented amounts of energy.
Green data centers represent a paradigm shift in how we approach digital infrastructure, combining cutting-edge technology with environmental consciousness. These innovative facilities are not just reducing carbon footprints—they’re reimagining the entire concept of sustainable computing for generations to come.
🌍 Understanding the Environmental Impact of Traditional Data Centers
Traditional data centers are energy-intensive operations that consume approximately 1-2% of global electricity usage. This massive consumption translates into significant carbon emissions, with many facilities relying heavily on fossil fuel-based power sources. The environmental impact extends beyond just electricity consumption, encompassing water usage for cooling systems, electronic waste generation, and the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing and transporting equipment.
The exponential growth of cloud computing, artificial intelligence, streaming services, and Internet of Things devices has created an insatiable demand for data processing and storage. Without intervention, experts predict that data centers could account for up to 8% of global electricity demand by 2030. This alarming projection has catalyzed the technology industry to seek sustainable alternatives that can support digital growth without compromising planetary health.
💡 What Defines a Green Data Center
A green data center is a facility specifically designed to minimize environmental impact through efficient technologies, renewable energy sources, and sustainable operational practices. These facilities prioritize energy efficiency at every level—from server hardware and cooling systems to building design and power management. The goal is to maximize computing performance while minimizing resource consumption and environmental degradation.
Green data centers incorporate multiple sustainability strategies simultaneously. They utilize renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Advanced cooling technologies replace traditional air conditioning systems, significantly decreasing water and energy usage. Intelligent workload management ensures servers operate at optimal efficiency, eliminating unnecessary power consumption during low-demand periods.
Key Components of Sustainable Data Infrastructure
The architecture of green data centers differs substantially from conventional facilities. Energy-efficient servers using low-power processors form the computational foundation, while innovative cooling systems employ techniques like free air cooling, liquid cooling, or evaporative cooling to maintain optimal temperatures without excessive energy expenditure. Smart power distribution systems minimize electrical losses, and sophisticated monitoring software tracks energy usage in real-time, identifying optimization opportunities.
Building design itself plays a crucial role in sustainability. Strategic location selection considers climate conditions, proximity to renewable energy sources, and access to natural cooling resources. Architectural features maximize natural ventilation and lighting, while advanced insulation materials maintain stable internal temperatures with minimal mechanical intervention.
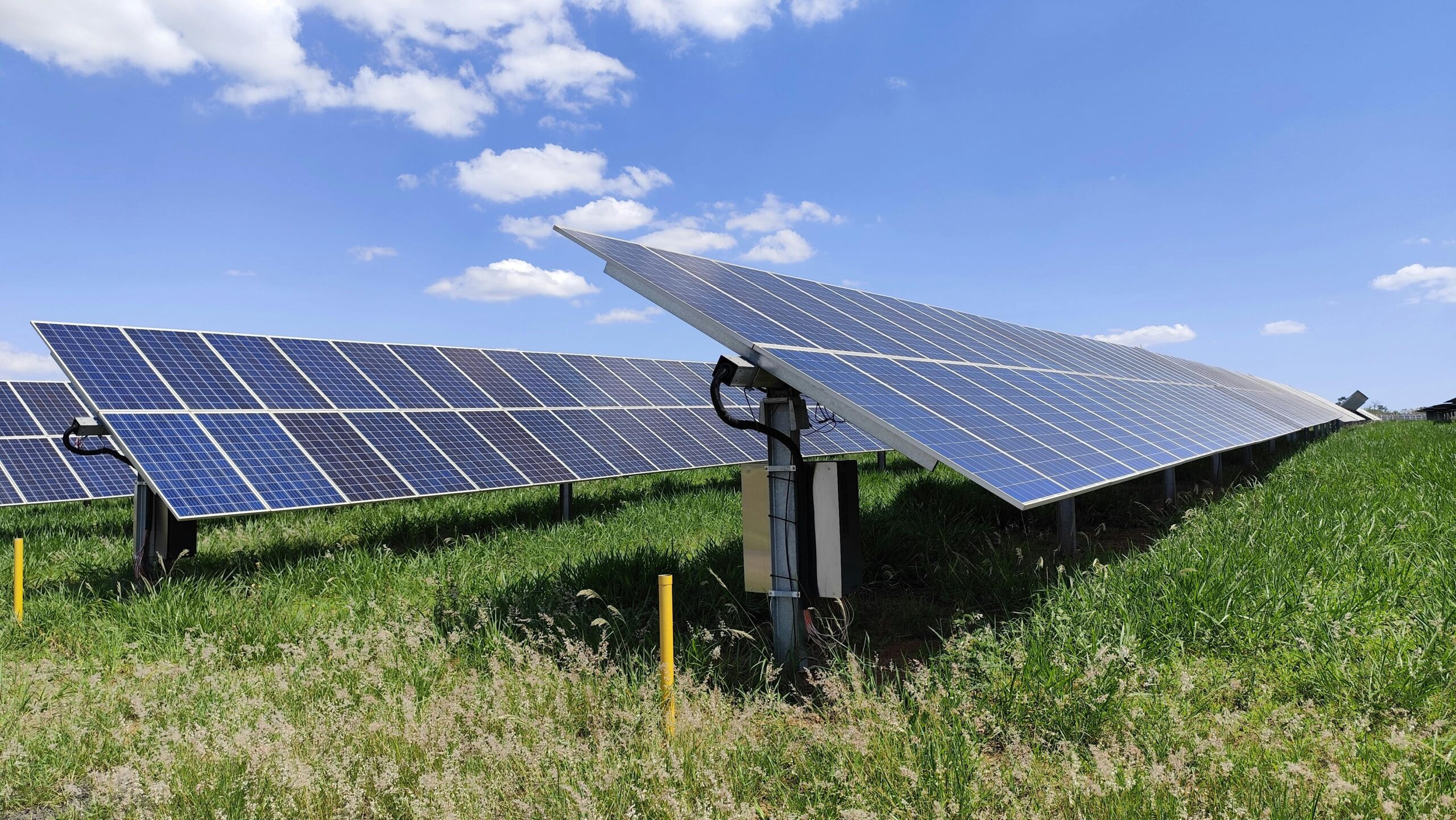
🔋 Renewable Energy Integration: The Power Behind Green Computing
Renewable energy integration stands as the cornerstone of green data center operations. Leading technology companies are investing billions in solar farms, wind installations, and hydroelectric projects to power their facilities with clean energy. This transition represents not merely an operational change but a fundamental reimagining of how digital infrastructure interacts with the broader energy ecosystem.
Some green data centers achieve 100% renewable energy usage through direct renewable generation on-site or through power purchase agreements with renewable energy providers. Solar panels on facility rooftops, nearby wind farms, or connections to hydroelectric grids ensure that every watt consumed originates from sustainable sources. This approach dramatically reduces carbon emissions while often providing long-term cost savings through stable energy prices.
Energy Storage and Grid Stability
Advanced battery storage systems enable green data centers to store excess renewable energy during peak generation periods and utilize it during high-demand times or when renewable sources are unavailable. This capability enhances grid stability and maximizes renewable energy utilization. Some facilities even participate in demand response programs, adjusting their energy consumption patterns to support overall grid health during peak usage periods.
❄️ Revolutionary Cooling Technologies Transforming Operations
Cooling systems traditionally consume 30-40% of total data center energy. Green facilities have revolutionized this aspect through innovative technologies that significantly reduce both energy consumption and environmental impact. Free air cooling leverages external air temperatures when conditions permit, eliminating mechanical cooling entirely during favorable weather. This technique proves particularly effective in temperate climates where ambient temperatures naturally support optimal server operation.
Liquid cooling systems represent another breakthrough technology. By circulating coolant directly to heat-generating components, these systems achieve superior thermal management with substantially less energy than traditional air conditioning. Some advanced implementations use immersion cooling, where servers operate completely submerged in non-conductive liquid, enabling unprecedented cooling efficiency and allowing higher-density computing configurations.
Waste Heat Recovery and Utilization
Progressive green data centers don’t merely manage heat—they capture and repurpose it. Waste heat recovery systems redirect thermal energy from servers to heat nearby buildings, greenhouses, or residential districts. This circular approach transforms what was once an environmental liability into a valuable resource, improving overall facility efficiency while providing sustainable heating solutions to surrounding communities.
📊 Measuring Sustainability: Metrics That Matter
Quantifying environmental performance requires sophisticated metrics that capture the multidimensional nature of sustainability. Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) remains the industry standard, measuring the ratio of total facility energy consumption to IT equipment energy consumption. While traditional data centers often operate with PUE values of 2.0 or higher, leading green facilities achieve values approaching 1.1, indicating minimal energy overhead beyond computing requirements.
However, PUE alone doesn’t capture the complete sustainability picture. Carbon Usage Effectiveness (CUE) measures greenhouse gas emissions per unit of IT energy consumed, providing critical insight into the carbon footprint regardless of total energy efficiency. Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE) quantifies water consumption for cooling and other operations, addressing growing concerns about water scarcity in many regions.
| Metric | Traditional Data Center | Green Data Center |
|---|---|---|
| PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) | 1.8 – 2.5 | 1.1 – 1.3 |
| Renewable Energy Usage | 0 – 20% | 80 – 100% |
| Annual Carbon Emissions | High | Near Zero |
| Water Consumption | Significant | Minimal to Zero |
🏢 Industry Leaders Driving the Green Revolution
Major technology corporations have emerged as pioneers in sustainable data infrastructure. Google has maintained carbon-neutral operations since 2007 and committed to operating entirely on carbon-free energy by 2030. Their data centers achieve industry-leading PUE values and incorporate machine learning algorithms to optimize cooling systems dynamically, reducing energy consumption by up to 40%.
Microsoft’s underwater data center project, Project Natick, explored the feasibility of submerged facilities cooled naturally by ocean water. Though experimental, this initiative demonstrates the industry’s willingness to explore unconventional solutions. The company has also committed to being carbon negative by 2030 and removing all historical carbon emissions by 2050.
Apple powers all its global facilities, including data centers, with 100% renewable energy. Their facilities in Denmark and Ireland use local renewable sources and feature innovative designs that eliminate traditional cooling systems entirely. Amazon Web Services, the world’s largest cloud provider, has committed to powering operations with 100% renewable energy by 2025 and is currently the largest corporate purchaser of renewable energy globally.
🌱 The Economic Case for Sustainable Infrastructure
Beyond environmental imperatives, compelling economic factors drive green data center adoption. Energy represents one of the largest operational expenses for data facilities, and efficiency improvements directly impact profitability. Renewable energy sources increasingly offer cost advantages over fossil fuels, with solar and wind electricity now cheaper than coal or natural gas in many markets.
Green certifications and sustainability credentials also provide marketing advantages and help attract environmentally conscious clients. Regulatory pressures and carbon pricing mechanisms in various jurisdictions make sustainable operations increasingly financially prudent. Companies demonstrating genuine environmental commitment often experience enhanced brand reputation, improved employee recruitment and retention, and better access to capital from ESG-focused investors.
Long-term Investment Returns
While initial capital investment for green data centers may exceed traditional facilities, long-term operational savings typically justify the upfront costs. Reduced energy expenses, lower cooling requirements, and decreased maintenance needs contribute to favorable return on investment. Additionally, future-proofing against potential carbon taxes and regulatory requirements provides valuable risk mitigation.
🚀 Emerging Technologies Shaping Tomorrow’s Data Centers
Innovation continues accelerating in sustainable data infrastructure. Artificial intelligence and machine learning optimize energy consumption in real-time, predicting demand patterns and adjusting operations proactively. These intelligent systems can reduce energy waste by identifying inefficiencies invisible to human operators and automatically implementing corrective measures.
Edge computing represents another transformative trend, distributing data processing closer to end-users rather than centralizing everything in massive facilities. This approach reduces transmission energy requirements and enables smaller, more efficient local data centers powered by renewable sources appropriate to their specific geographic contexts.
- Hydrogen fuel cells offering clean backup power alternatives to diesel generators
- Advanced materials improving thermal management and energy efficiency
- Quantum computing potentially revolutionizing computational efficiency
- Modular data center designs enabling rapid deployment and scalability
- Blockchain-based systems for transparent energy tracking and carbon accounting
🌐 Global Policy and Regulatory Landscape
Governments worldwide are recognizing data center environmental impacts and implementing policies to encourage sustainability. The European Union’s Green Deal includes specific provisions targeting data center efficiency, with proposed regulations requiring facilities to meet minimum energy performance standards and report environmental metrics transparently.
Singapore, despite its tropical climate presenting cooling challenges, has established a Green Data Centre Roadmap with ambitious efficiency targets. The country temporarily paused new data center development to assess environmental impact and ensure future facilities meet stringent sustainability criteria. Similar regulatory frameworks are emerging across Asia, North America, and other regions as policymakers balance digital infrastructure needs with environmental responsibilities.
🔮 The Path Forward: Building a Sustainable Digital Future
The transition to green data centers represents more than incremental improvement—it embodies a fundamental reimagining of digital infrastructure’s relationship with the natural environment. As data consumption continues growing exponentially, sustainability isn’t optional but essential for the technology sector’s long-term viability.
Achieving truly sustainable digital infrastructure requires continued innovation, substantial investment, and collaborative efforts across industries and governments. Technology providers, energy companies, policymakers, and consumers all play vital roles in this transformation. The choices made today regarding data center design, operation, and regulation will determine whether digital growth remains compatible with planetary health.
The rise of green data centers demonstrates that environmental responsibility and technological advancement aren’t opposing forces but complementary objectives. These facilities prove that with creativity, commitment, and appropriate investment, we can power the digital future without compromising the natural world. As more organizations embrace sustainable practices and technologies continue evolving, green data centers will transition from innovative exceptions to industry standards, ensuring that our increasingly digital world operates in harmony with the environment that sustains us all.
The revolution in sustainable data infrastructure has begun, driven by environmental necessity, economic opportunity, and technological possibility. The future of computing will be green—not because regulations mandate it or marketing demands it, but because intelligent design, operational efficiency, and environmental stewardship create superior outcomes for businesses, communities, and the planet. This transformation represents one of the most significant opportunities to align technological progress with ecological responsibility, powering a cleaner, smarter future for all. 🌟
Toni Santos is a science communicator and sustainability writer exploring the relationship between materials, innovation, and environmental ethics. Through his work, Toni highlights how engineering and research can build a more responsible technological future. Fascinated by the evolution of materials and clean technologies, he studies how design, science, and sustainability converge to redefine progress. Blending material science, environmental design, and cultural insight, Toni writes about innovation that respects both precision and planet. His work is a tribute to: The ingenuity driving material and technological advancement The balance between progress and environmental responsibility The creative spirit shaping sustainable industry Whether you are passionate about innovation, sustainability, or material science, Toni invites you to explore the frontier of technology — one discovery, one design, one breakthrough at a time.




